表签
1. lucene 简介
1.1. 搜索引擎的历史
- 萌芽:Archie、Gopher
- 起步:Robot(网络机器人)的出现与Spider(网络爬虫)
- 发展:Excite、Galaxy、Yahoo等
- 繁荣:Infoseek、AltaVista、Google和Baidu
1.2. 什么是Lucene
- Lucene是非常优秀的成熟的 开源的 免费的纯 纯java 语言的全文索引检索工具包。
- 全文检索 是指计算机索引程序通过扫描文章中的每一个词,对每一个词建立一个索引,指明该词在文章中出现的次数和位置,当用户查询时,检索程序就根据事先建立的索引进行查找,并将查找的结果反馈给用户的检索方式。
- Lucene是一个高性能、可伸缩的信息搜索(IR)库。 Information Retrieval(IR) library.它使你可以为你的应用程序添加索引和搜索能力。
- Lucene的作者Doug Cutting是资深的全文索引/检索专家,最开始发布在他本人的主页上,2001年10月贡献给APACHE,成为APACHE基金的一个子项目。http://jakarta.apache.org/lucene/
- Lucene是一个IR库而不是现成的产品,当然也不是Lucene的初识者常常认为的web爬行器
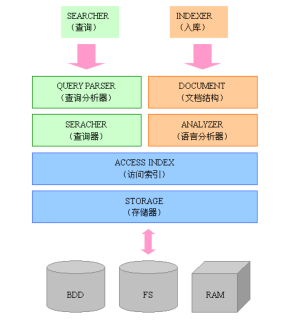
1.3. 全文检索系统的结构
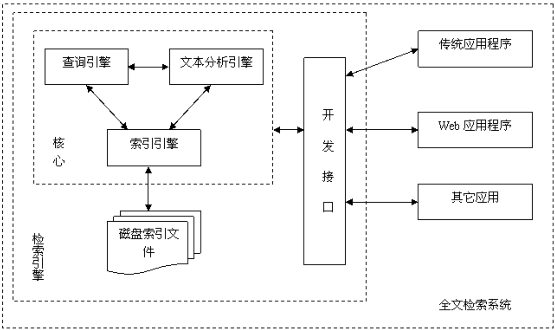
1.4. 为什么使用Lucene
- Lucene作为一个全文检索引擎,其具有如下突出的优点:
- 索引文件格式独立于应用平台。Lucene定义了一套以8位字节为基础的索引文件格式,使得兼容系统或者不同平台的应用能够共享建立的索引文件。
- 在传统全文检索引擎的 倒排索引的基础上,实现了分块索引,能够针对新的文件建立小文件索引,提升索引速度。然后通过与原有索引的合并,达到优化的目的。
- 优秀的面向对象的系统架构,使得对于Lucene扩展的学习难度降低,方便扩充新功能。
- 设计了独立于语言和文件格式的文本分析接口,索引器通过接受Token流完成索引文件的创立,用户 扩展新的语言和文件格式,只需要实现文本分析的接口。
- 已经默认实现了一套强大的 查询引擎,用户无需自己编写代码即使系统可获得强大的查询能力,Lucene的查询实现中默认实现了布尔操作、模糊查询(Fuzzy Search)、分组查询等等。
- 开源, 可扩展能力强,有各种语言版本,适合各种平台,
1.5. Lucene 倒排索引原理
- 假设有两篇文章1和2 文章1的内容为:Tom lives in Guangzhou,I live in Guangzhou too. 文章2的内容为:He once lived in Shanghai.
- 经过分词处理后 文章1的所有关键词为:[tom] [live] [guangzhou] [i] [live] [guangzhou] 文章2的所有关键词为:[he] [live] [shanghai]
- 加上“出现频率”和“出现位置”信息后,我们的索引结构为:
| 关键词 | 文章号[出现频率] | 出现位置 |
|---|---|---|
| guangzhou | 1[2] | 3,6 |
| he | 2[1] | 1 |
| i | 1[1] | 4 |
| live | 1[2],2[1] | 2,5,2 |
| shanghai | 2[1] | 3 |
| tom | 1[1] | 1 |
1.6. Lucene只关注文本的索引和搜索
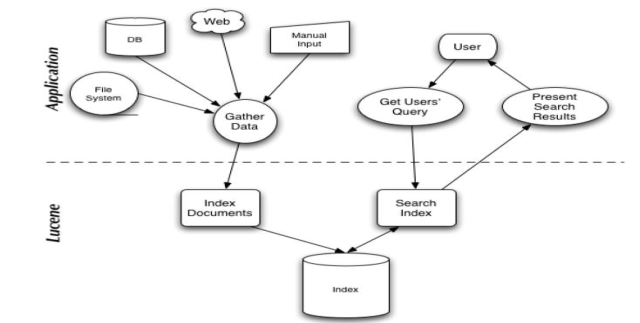
1.7. Lucene Implementations
- Lucene implementations in languages other than Java:
- CLucene - Lucene implementation in C++
- dotLucene - Lucene implementation in .NET
- Lucene4c - Lucene implementation in C
- LuceneKit - Lucene implementation in Objective-C (Cocoa/GNUstepsupport)
- Lupy - Lucene implementation in Python (RETIRED)
- NLucene - another Lucene implementation in .NET (out of date)
- Zend Search - Lucene implementation in the Zend Framework for PHP 5
- Plucene - Lucene implementation in Perl
- KinoSearch - a new Lucene implementation in Perl
- PyLucene - GCJ-compiled version of Java Lucene integrated with Python
- MUTIS - Lucene implementation in Delphi
- Ferret - Lucene implementation in Ruby
1.8. 基于Lucene的搜索程序
Applications and web applications using Lucene include (alphabetically) :
- ActiveMath - a user adaptive, interactive and web-based learning environment for mathematics
- Aduna AutoFocus - a visual desktop search tool
- Aduna Metadata Server - RDF-based indexing server for metadata and full text
- Ahahi - a search engine (web,news,image,forum,crawler)
- Affiliate Ranker - an affiliate program search engine
- Bigsearch.ca - uses nutch, based on lucene open source software to deliver its search results.
- BibleDesktop - A Bible study program using lucene to search Bibles
- Bixee - Search Engine for Jobs in India.
- BNCF Opac - Online Public Access Catalog, indexing data in unimarcslim format
- Australia Unclassified - Australia's 100% FREE online classifieds service
- Celoxis - web based project management tool
- CodeCrawler - is a smart, web-based search engine specifically built for use by developers for searching source code.
- Coolposting - a search engine for discussion forums. Coolposting helps you find the real solutions, experiences and opinions people have posted in different discussion forums.
- Corinis CCM - a web content management and community system
- CvMail - web based tool for recruiters (to manage job-applications by mail)
- ……
1.9. Compass
- 已加入Opensymphony的Compass 是对Lucene搜索引擎在企业应用(数据库应用)中的增强。
- 你能大概给我们讲解一下Nutch 吗?以及你将在哪方面运用它?
- 我还是先说一下Lucene吧。Lucene其实是一个提供全文文本搜索的函数库,它不是一个应用软件。它提供很多API函数让你可以运用到各种实际应用程序中。现在,它已经成为Apache的一个项目并被广泛应用着。这里列出一些已经使用Lucene的系统。
- Nutch 是一个建立在Lucene 核心之上的Web 搜索的实现,它是一个真正的应用程序。也就是说,你可以直接下载下来拿过来用。它在Lucene的基础上加了网 络爬虫和一些和Web相关的东东。其目的就是想从一个简单的站内索引和搜索推广到全球网络的搜索上,就像Google和Yahoo一样。当然,和那些巨人 竞争,你得动一些脑筋,想一些办法。我们已经测试过100M的网页,并且它的设计用在超过1B的网页上应该没有问题。当然,让它运行在一台机器上,搜索一些服务器,也运行的很好。
1.11. 开源搜索引擎列表
http://www.open-open.com/32.htm
- Egothor Egothor是一个用Java编写的开源而高效的全文本搜索引擎。借助Java的跨平台特性,Egothor能应用于任何环境的应用,既可配置为单独的搜索引擎,又能用于你的应用作为全文检索之用。
- Nutch Nutch 是一个开源Java 实现的搜索引擎。它提供了我们运行自己的搜索引擎所需的全部工具。包括全文搜索和Web爬虫。
- Lucene Apache Lucene是一个基于Java全文搜索引擎,利用它可以轻易地为Java软件加入全文搜寻功能。Lucene的最主要工作是替文件的每一个字作索引,索 引让搜寻的效率比传统的逐字比较大大提高,Lucen提供一组解读,过滤,分析文件,编排和使用索引的API,它的强大之处除了高效和简单外,是最重要的 是使使用者可以随时应自已需要自订其功能。
- Oxyus 是一个纯java写的web搜索引擎。
- BDDBot BDDBot是一个简单的易于理解和使用的搜索引擎。它目前在一个文本文件(urls.txt)列出的URL中爬行,将结果保存在一个数据库中。它也支持一个简单的Web服务器,这个服务器接受来自浏览器的查询并返回响应结果。它可以方便地集成到你的Web站点中。
- Zilverline Zilverline 是一个搜索引擎,它通过web方式搜索本地硬盘或intranet上的内容。Zilverline可以从PDF, Word, Excel, Powerpoint, RTF, txt, java, CHM,zip, rar等文档中抓取它们的内容来建立摘要和索引。从本地硬盘或intranet中查找到的结果可重新再进行检索。Zilverline支持多种语言其中包 括中文。
- XQEngine XQEngine 用于XML文档的全文本搜索引擎.利用XQuery做为它的前端查询语言.它能够让你查询XML文档集合通过使用关键字的逻辑组合.有点类似于 Google与其它搜索引擎搜索HTML文档一样.XQEngine只是一个用Java开发的很紧凑的可嵌入的组件.
- MG4J MG4J可以让你为大量的文档集合构建一个被压缩的全文本索引,通过使内插编码(interpolative coding)技术。
- JXTA Search JXTA Search是一个分布式的搜索系统.设计用在点对点的网络与网站上.
- YaCy YaCy基于p2p的分布式Web搜索引擎.同时也是一个Http缓存代理服务器.这个项目是构建基于p2pWeb索引网络的一个新方法.它可以搜索你自己的或全局的索引,也可以Crawl自己的网页或启动分布式Crawling等.
- Red-Piranha Red -Piranha是一个开源搜索系统,它能够真正"学习"你所要查找的是什么.Red-Piranha可作为你桌面系统(Windows,Linux与 Mac)的个人搜索引擎,或企业内部网搜索引擎,或为你的网站提供搜索功能,或作为一个P2P搜索引擎,或与wiki结合作为一个知识/文档管理解决方 案,或搜索你要的RSS聚合信息,或搜索你公司的系统(包括SAP,Oracle或其它任何Database/Data source),或用于管理PDF,Word和其它文档,或作为一个提供搜索信息的WebService或为你的应用程序(Web,Swing,SWT, Flash,Mozilla-XUL,PHP,Perl或c#/.Net)提供搜索后台等等.
- LIUS LIUS是一个基于Jakarta Lucene项目的索引框架。LIUS为Lucene添加了对许多文件格式的进行索引功能如:
- Ms Word,Ms Excel,Ms PowerPoint,RTF,PDF,XML,HTML,TXT,Open Office序列和JavaBeans。针对
- JavaBeans的索引特别有用当我们要对数据库进行索引或刚好用户使用持久层ORM技术如:Hibernate,JDO,Torque,TopLink进行开发时。
- Aperture Aperture这个Java框架能够从各种各样的资料系统(如:文件系统、Web站点、IMAP和Outlook邮箱)或存在这些系统中的文件(如:文档、图片)爬取和搜索其中的全文本内容与元数据。
- Apache Solr Solr 是一个高性能,采用Java5开发,基于Lucene的全文搜索服务器。文档通过Http利用XML加到一个搜索集合中。查询该集合也是通过http收到 一个XML/JSON响应来实现。它的主要特性包括:高效、灵活的缓存功能,垂直搜索功能,高亮显示搜索结果,通过索引复制来提高可用性,提供一套强大 Data chema来定义字段,类型和设置文本分析,提供基于Web的管理界面等。
- Paoding Paoding中文分词是一个使用Java开发的,可结合到Lucene应用中的,为互联网、企业内部网使用的中文搜索引擎分词组件。Paoding填补了国内中文分词方面开源组件的空白,致力于此并希翼成为互联网网站首选的中文分词开源组件。 Paoding中文分词追求分词的高效率和用户良好体验。
1.12. 全球商用搜索市场
- 公司创始人麦克林奇:在全球商用搜索市场上,Autonomy是老大!Autonomy的市值不足Google的零头,而Google在这一市场的份额也不足Autonomy份额的零头.我们拥有55%的份额,而且这些份额的一半以上来自Google的母国:美国。”林奇说,尽管Google在全球消费搜索市场上取得了巨大成功,但在商用搜索市场上的份额仅为1%。
- 一位微软研发专家透露,在企业搜索领域,Autonomy的技术排名第一。“百度、谷歌等互联网搜索不是真正的搜索引擎,只能称为搜索服务。”
1.13. 推荐文章
- 《擎 开发自己的搜索引擎——Lucene2.0+Heritrix 》
- 《Lucene in Action 》
- 《Doug Cutting 访谈录 -- 关于搜索引擎的开发 》
1.14. Heritrix介绍
1.15. 课堂练习:Heritrix简单抓取任务的设置
2. 入门实例
2.1. 安装-压缩包内容
- lucene-core-XX.jar
- The compiled lucene library.
- lucene-demos-XX.jar
- The compiled simple example code.
- luceneweb.war
- The compiled simple example Web Application.
- contrib/*
- Contributed code which extends and enhances Lucene, but is not
- part of the core library. Of special note are the JAR files in the analyzers and snowball directory which
- contain various analyzers that people may find useful in place of the StandardAnalyzer.
- docs/index.html
- The contents of the Lucene website.
- docs/api/index.html
- The Javadoc Lucene API documentation. This includes the core library, the demo, as well as all of the contrib modules.
- src/java
- The Lucene source code.
- src/demo
- Lucene 的系统由基础结构封装、索引核心、对外接口三大部分组成.
- 其中直接操作索引文件的索引核心又是系统的重点。
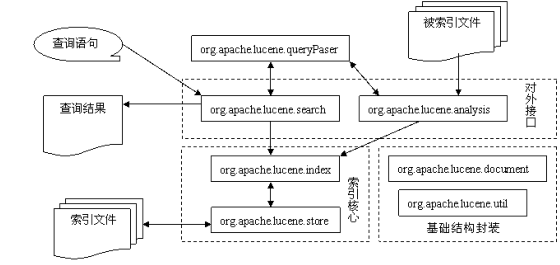
2.4. Lucene包结构功能表
- lucene-core-2.2.0.jar
| 包名 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| org.apache.lucene.analysis | 语言分析器,主要用于的切词,支持中文主要是扩展此类 |
| org.apache.lucene.document | 索引存储时的文档结构管理,类似于关系型数据库的表结构 |
| org.apache.lucene.index | 索引管理,包括索引建立、删除等 |
| org.apache.lucene.queryParser | 查询分析器,实现查询关键词间的运算,如与、或、非等 |
| org.apache.lucene.search | 检索管理,根据查询条件,检索得到结果 |
| org.apache.lucene.store | 数据存储管理,主要包括一些底层的I/O操作 |
| org.apache.lucene.util | 一些公用类 |
2.5. Lucene 的主要逻辑图
- Lucene功能强大,但从根本上说,主要包括两块:
- 查询者输入查询条件,条件之间可以通过特定运算符进行运算,比如查询希望查询到与“中国”和“北京”相关的记录,但不希望结果中包括“海淀区中关村”,于是输入条件为“国 中国+ 北京- 海淀区中关村”;
- 查询条件被传达到查询分析器中,分析器将将对“中国+北京-海 淀区中关村”进行分析,首先分析器解析字符串的连接符,即这里的加号和减号,然后对每个词进行切词,一般最小的词元是两个汉字,则中国和北京两个词不必再 切分,但对海淀区中关村需要切分,假设根据切词算法,把该词切分为“海淀区”和“中关村”两部分,则最后得到的查询条件可以表示为:” “中国” AND “ 北京” ANDNOT (“海淀区” AND “ 中关村”)。
- 查询器根据这个条件遍历索引树,得到查询结果,并返回结果集,返回的结果集类似于JDBC中的ResultSet。
- 将返回的结果集显示在查询结果页面,当点击某一条内容时,可以链接到原始网页,也可以打开全文检索库中存储的网页内容。
- 这就是查询的逻辑过程,需要说明的是,Lucene 默认只支持英文,为了便于说明问题,以上查询过程采用中文举例,事实上,当Lucene被扩充支持中文后就是这么一个查询过程。
2.7. 入库逻辑
- 入 库者定义到库中文档的结构,比如需要把网站内容加载到全文检索库,让用户通过“站内检索”搜索到相关的网页内容。入库文档结构与关系型数据库中的表结构类 似, 每个入库的文档由多个字段构成,假设这里需要入库的网站内容包括如下字段:文章标题、作者、发布时间、原文链接、正文内容(一般作为网页快照)。
- 包含N个字段的文档(DOCUMENT) 在真正入库前需要经过切词(或分词)索引,切词的规则由语言分析器(ANALYZER)完成。
- 切分后的“单词”被注册到索引树上,供查询时用,另外也需要把其它不需要索引的内容入库,所有这些是文件操作均由STORAGE完成。
- Lucene的索引树结构非常优秀,是Lucene的一大特色。
2.8. 理解核心索引类
- 为了对文档进行索引,Lucene 提供了五个基础的类
- public class IndexWriter
- org.apache.lucene.index.IndexWriter
- public abstract class Directory
- org.apache.lucene.store.Directory
- public abstract class Analyzer
- org.apache.lucene.analysis.Analyzer
- public final class Document
- org.apache.lucene.document.Document
- public final class Field
- public class IndexWriter
- IndexWriter是在索引过程中的中心组件。
- IndexWriter这个类创建一个新的索引并且添加文档到一个已有的索引中。把 你可以把IndexWriter 想象成让你可以对索引进行写操作的对象,但是不能让你读取或搜索。
- IndexWriter不是唯一的用来修改索引的类
- org.apache.lucene.index.IndexWriter
- public IndexWriter(String path, Analyzer a, boolean create) ……
- Parameters:
- 在一个文档被索引之前,首先需要对文档内容进行分词处理,并且而剔除一些冗余的词句(例如:a,the,they等),这部分工作就是由 Analyzer 来做的。
- Analyzer 类是一个抽象类,它有多个实现。 BrazilianAnalyzer, ChineseAnalyzer, CJKAnalyzer, CzechAnalyzer,DutchAnalyzer, FrenchAnalyzer, GermanAnalyzer, GreekAnalyzer,KeywordAnalyzer, PatternAnalyzer, PerFieldAnalyzerWrapper,RussianAnalyzer, SimpleAnalyzer, SnowballAnalyzer,StandardAnalyzer, StopAnalyzer, ThaiAnalyzer, hitespaceAnalyzer
- 针对不同的语言和应用需要选择适合的 Analyzer。Analyzer 把分词后的内容交给 IndexWriter 来建立索引。
2.11. Document
- org.apache.lucene.document.Document
- Document文档类似数据库中的一条记录,可以由好几个字段(Field)组成,并且字段可以套用不同的类型。
- 一个Field代表与这个文档相关的元数据。元数据如作者、标题、主题、修改日期等等,分别做为文档的字段索引和存储。
- Document的方法:
- org.apache.lucene.document.Field
- Field 对象是用来描述一个文档的某个属性的,比如一封电子邮件的标题和内容个 可以用两个 Field 对象分别描述。
- Field(String name, byte[] value, Field.Store store)Create a stored field with binary value.
- Field(String name, Reader reader)Create a tokenized and indexed field that is not stored.
- Field(String name, Reader reader, Field.TermVector termVector)Create a tokenized and indexed field that is not stored, optionally with storing term vectors.
- Field(String name, String value, Field.Store store, Field.Index index)Create a field by specifying its name, value and how it will be saved in the index.
- Field(String name, String value, Field.Store store, Field.Index index,Field.TermVector termVector)Create a field by specifying its name, value and how it will be saved in the index.
- Field(String name, TokenStream tokenStream)Create a tokenized and indexed field that is not stored.
- Field(String name, TokenStream tokenStream, Field.TermVector termVector)Create a tokenized and indexed field that is not stored, optionally with storing term vectors.
2.13. 静态内部类
- Field.Index 表示Field的索引方式
- NO 表示该Field不需要索引,也就是用户不需要去查找该Field的值
- NO_NORMS 表示对该Field进行索引,但是不使用Analyzer,同时禁止它参加评分,主要是为了减少内存的消耗
- TOKENIZED 表示该Field先被分词再索引
- UN_TOKENIZED 像链接地址URL、文件系统路径信息、时间日期、人名、居民身份证、电话号码等等通常将被索引并且完整的存储在索引中,但一般不需要切分词
- Field.Store 表示Field的存储方式
- COMPRESS压缩存储
- NO 原文不存储在索引文件中,搜索结果命中后,再根据其他附加属性如文件的Path,数据库的主键等,重新连接打开原文,适合原文内容较大的情况。
YES索引文件本来只存储索引数据, 此设计将原文内容直接也存储在索引文件中,如文档的标题。
2.14. 创建一个索引的大致过程
IndexWriter writer = new IndexWriter(INDEX_DIR,new StandardAnalyzer(), true); Document doc = new Document(); doc.add(new Field(***)); writer.addDocument(doc); writer.optimize();//合并索引并优化 writer.close();2.15. 课堂练习:建立一个索引
- org.apache.lucene.demo.html.HTMLParser
File f = new File(root); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f); HTMLParser parser = new HTMLParser(fis); doc.add(new Field("contents", parser.getReader())); doc.add(new Field("summary", parser.getSummary(), Field.Store.YES, Field.Index.NO)); doc.add(new Field("title", parser.getTitle(), Field.Store.YES,Field.Index.TOKENIZED));2.16. java.lang.OutOfMemoryError
- Exception in thread "main" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space
- at org.apache.lucene.demo.html.SimpleCharStream.
(SimpleCharStream.java:245) - at org.apache.lucene.demo.html.SimpleCharStream.
(SimpleCharStream.java:292) - at org.apache.lucene.demo.html.SimpleCharStream.
(SimpleCharStream.java:298) - at org.apache.lucene.demo.html.HTMLParser.
(HTMLParser.java:490) - at IndexHTML.indexDoc(IndexHTML.java:35)
- at IndexHTML.indexDocs(IndexHTML.java:30)
- at IndexHTML.indexDocs(IndexHTML.java:27)
- at IndexHTML.indexDocs(IndexHTML.java:27)
- at IndexHTML.indexDocs(IndexHTML.java:27)
- at IndexHTML.indexDocs(IndexHTML.java:27)
- at IndexHTML.indexDocs(IndexHTML.java:27)
- at IndexHTML.indexDocs(IndexHTML.java:27)
- at IndexHTML.indexDocs(IndexHTML.java:27)
- at IndexHTML.main(IndexHTML.java:18)
-Xmx512m
2.17. 理解核心搜索类
- 只需要几个类来执行基本的搜索操作:
- public class IndexSearcher
- org.apache.lucene.search.IndexSearcher extends Searcher
- public final class Term
- org.apache.lucene.index.Term
- public abstract class Query
- org.apache.lucene.search.Query
- public class TermQuery
- org.apache.lucene.search.TermQuery extends Query
- public final class Hits
- public class IndexSearcher
- IndexSearcher是用来在建立好的索引上进行搜索的
- 它只能以只读的方式打开一个索引,所以可以有多个IndexSearcher的实例在一个索引上进行操作。
- 它提供几个搜索方法,其中一些在抽象基类Searcher中实现;
2.19. Search方法
- 返回值为Hits型的对象:
- public final Hits search(Query query) throws IOException
- Returns the documents matching query.
- public Hits search(Query query, Filter filter) throws IOException
- Returns the documents matching query and filter.
- public Hits search(Query query, Sort sort) throws IOException
- Returns documents matching query sorted by sort.
- public Hits search(Query query, Filter filter, Sort sort) throws IOException
- public final Hits search(Query query) throws IOException
- 返回索引中得分较高的文档集合,这些方法中,都带有一个int形式参数,表示取出置于TopDocs集合中的文档数量
- public TopDocs search(Query query, Filter filter, int n) throws IOException
- public abstract TopDocs search(Weight weight, Filter filter, int n) throws IOException
- public TopFieldDocs search(Query query, Filter filter, int n, Sort sort) throws IOException
- public abstract TopFieldDocs search(Weight weight, Filter filter, int n, Sort sort) throws IOException
- public void search(Query query, Filter filter, HitCollector results) throws IOException
- public void search(Query query, HitCollector results) throws IOException
- public abstract void search(Weight weight, Filter filter, HitCollector results) throws IOException
2.20. Term
- Term是 搜索的基本单元。一个Term对象有两个String类型的域组成:字段的名称和字段的值。
- 在搜索时,你可能创建Term对象并和TermQuery同时使用。其中第一个参数代表了要在文档的哪一个Field上进行查找,第二个参数代表了要查询的关键词。
Query q = new TermQuery(new Term(“fieldName”, “queryWord ”)); Hits hits = sercher.search(q); - 这段代码使Lucene找出在fieldName字段中含有单词queryWord的所有文档。因为TermQuery对象继承自它的抽象父类Query,你可以在等式的左边用Query类型。
2.21. Query
- Query是一个抽象类,这个类的目的是把用户输入的查询字符串封装成Lucene能够识别的Query。
- Lucene中包含一些Query的具体子类。Direct Known Subclasses:
- BooleanQuery, BoostingQuery, ConstantScoreQuery,ConstantScoreRangeQuery, CustomScoreQuery,DisjunctionMaxQuery, FilteredQuery, FuzzyLikeThisQuery,MatchAllDocsQuery, MoreLikeThisQuery, MultiPhraseQuery,MultiTermQuery, PhraseQuery, PrefixQuery, RangeQuery, SpanQuery,TermQuery, ValueSourceQuery
2.22. TermQuery
- BooleanQuery, BoostingQuery, ConstantScoreQuery,ConstantScoreRangeQuery, CustomScoreQuery,DisjunctionMaxQuery, FilteredQuery, FuzzyLikeThisQuery,MatchAllDocsQuery, MoreLikeThisQuery, MultiPhraseQuery,MultiTermQuery, PhraseQuery, PrefixQuery, RangeQuery, SpanQuery,TermQuery, ValueSourceQuery
- TermQuery是抽象类Query的一个子类,它同时也是Lucene支持的最为基本的一个查询类。
- 生成一个TermQuery对象由如下语句完成:
它的构造函数只接受一个参数,那就是一个Term对象。
TermQuery termQuery = new TermQuery(new Term(“fieldName”,”queryWord”));2.23. Hits
- Hits是用来保存搜索的结果的。
- 基于性能考虑,Hits的实例并不从索引中加载所有匹配查询的所有文档,而是每次一小部分。
public final int length() public final Document doc(int n)… public final float score(int n)… public final int id(int n)… public Iterator iterator()2.24. 关键词搜索的大致过程
- 最简单的接受单个Query对象做为参数并返回一个Hits对象。这个方法的典型应用类似这样:
IndexSearcher sercher = new IndexSearcher( INDEX_DIR); Query q = new TermQuery(new Term(“contents”, “lucene”)); Hits hits = sercher.search(q); for (int i = 0; i < hits.length(); i++) { Document doc = hits.doc(i); String summary = doc.get(“title"); }2.25. 课堂练习:简单的关键词搜索
2.26. 项目实践:构建一个简单的WEB搜索程序
3. 内建Query 对象
3.1. BooleanQuery布尔搜索
- BooleanQuery是实际开发过程中经常使用的一种Query。
- 它其实是一个组合的Query,在使用时可以把各种Query对象添加进去并标明它们之间的逻辑关系。
- BooleanQuery是可以嵌套的(BooleanQuery是一个布尔子句的容器)
- public void add(Query query, BooleanClause.Occur occur)
- BooleanClause用于表示布尔查询子句关系的类,包括:
- BooleanClause.Occur.MUST,BooleanClause.Occur.MUST_NOT,
- BooleanClause.Occur.SHOULD。
- 有以下6种组合:
- public RangeQuery(Term lowerTerm, Term upperTerm,boolean inclusive)
- 布尔型的参数表示是否将2个临界值也加入到搜索中
- 查找所有书号在000001到000005之间的图书,并且不包括000001和000005
IndexSearcher searcher = new IndexSearcher(PATH); Term begin = new Term("booknumber","000001"); Term end = new Term("booknumber","000005"); RangeQuery query = new RangeQuery(begin,end,false); Hits hits = searcher.search(query);3.4. PrefixQuery 前缀搜索
- 《钢铁是怎样炼成的》《英雄儿女》《篱笆女人和狗》《女人是水做的》《我的兄弟和女儿》《白毛女》《钢的世界》《钢铁战士》
- 《钢铁是怎样炼成的》 , 《钢铁战士》 , 《钢和铁是两种金属元素》 , 《钢要比铁有更多的碳元素》 , 《铁和钢是两种重要的金属》 , 《铁钢是两种重要的金属》
- 《钢铁战士》,《钢铁是怎样炼成的》
IndexSearcher searcher = new IndexSearcher(PATH); PhraseQuery query = new PhraseQuery(); query.add(new Term("bookname","钢")); query.add(new Term("bookname","铁")); Hits hits = searcher.search(query);
- 《钢铁战士》,《钢铁是怎样炼成的》
- 可以看出,搜索的结果都是“钢”和“铁”两字相连,而且顺序也一致的文档,即严格包含有“钢铁”这个短语的文档
- PhraseQuery提供了一种为“坡度”的参数,用于表示词组的两个字之间可以插入无关单字的个数。
- word,work,world,seed,sword,ford
- work -> work,word
- FuzzyQuery(Term term) Calls FuzzyQuery(term, 0.5f, 0).
- FuzzyQuery(Term term, float minimumSimilarity) Calls FuzzyQuery(term, minimumSimilarity, 0). minimumSimilarity参数代表:最小相似度。默认为0.5。数值越小,文档数量越多。相似度为1时, FuzzyQuery变成了TermQuery。
- FuzzyQuery(Term term, float minimumSimilarity, int prefixLength)
prefixLength参数代表:要有多少个前缀字母必须完全其配。
3.7. WildcardQuery通配符搜索
- *代表0到多个字符,?代表一个单一的字符
IndexSearcher searcher = new IndexSearcher(PATH); Term t = new Term("content","?o*"); WildcardQuery query = new WildcardQuery(t); Hits hits = searcher.search(query);3.8. SpanQuery 跨度搜索
- Man always remember love because of romance only
- 每个term 均有一个位置:Man 是1 ,always 是2 ,remember 是3……
- 如果跨度为3 ,则应该包括Man always remember 3 个term 。
- 在某种跨度范围内,查找关键词并匹配文档,称为跨度搜索
- SpanQuery 是一个抽象类,实际的搜索功能由它的子类完成。
3.9. ____RegexQuery正则表达式搜索
- 涉及2 个包:
- Package org.apache.lucene.search.regex
- Package org.apache.regexp
- 注意:
- /contrib/regex/lucene-regex-2.2.0.jar 放入工程。
- jakarta-regexp-1.5.jar
String regex = "http://[a-z]{1,3}\\.abc\\.com/.*"; Term t = new Term("url",regex); RegexQuery query = new RegexQuery(t);3.10. ____MultiFieldQueryParser 多域搜索
- org.apache.lucene.queryParser.MultiFieldQueryParser
- 在不同的Field上进行不同的查找
- public static Query parse(String[] queries, String[] fields, Analyzer analyzer) throws ParseException
- 在不同的Field上进行同一个查找,指定他们之间的布尔关系
- public static Query parse(String query, String[] fields, BooleanClause.Occur[] flags, Analyzer analyzer) throws ParseException
- 在不同的Field上进行不同的查找,指定他们之间的布尔关系
- public static Query parse(String[] queries, String[] fields,BooleanClause.Occur[] flags, Analyzer analyzer) throws ParseException
3.11. ____MultiSearcher多索引搜索
IndexSearcher searcher1 = new IndexSearcher(PATH1); IndexSearcher searcher2 = new IndexSearcher(PATH2); IndexSearcher [] searchers = {searcher1,searcher2}; MultiSearcher searcher = new MultiSearcher(searchers); Hits hits = searcher.search(query);3.12. ____ParallelMultiSearcher多线程搜索
IndexSearcher searcher1 = new IndexSearcher(PATH1); IndexSearcher searcher2 = new IndexSearcher(PATH2); IndexSearcher [ ] searchers = {searcher1,searcher2}; ParallelMultiSearcher searcher = new ParallelMultiSearcher(searchers); Hits hits = searcher.search(query);3.13. 课堂练习:熟悉Lucene各种内建的Query对象
- public static Query parse(String[] queries, String[] fields,BooleanClause.Occur[] flags, Analyzer analyzer) throws ParseException
4. 分析器Analyzer
4.1. YACC -> JavaCC
- Lucene 很明智的避开了语言分析这个复杂的领域,转而使用JavaCC为其构造标准的分词器.
- JavaCC:JavaCompilerCompiler,纯Java的词法分析生成器.
- 对于JavaCC来说,只要为其提供一个后缀为.jj的文法描述文件,它就可以自动生成对应于该文法的解析器.
- Package org.apache.lucene.analysis.standard
- A grammar-based tokenizer constructed with JavaCC.
- Package org.apache.lucene.analysis.standard
- 如果从源代码编译或需要修改其中的QueryParser、定制自己的词法分析器,还需要下载javacc。
4.2. 英文分析器比较
xy&z mail is - [email protected]
- WhitespaceAnalyzer
- 空格分割
- xy&z,mail,is,-,[email protected]
- SimpleAnalyzer
- 空格及各种符号分割
- Xy,z,mail,is,xyz,sohu,com
- StopAnalyzer
- 空格及各种符号分割,去掉停止词,停止词包括 is,are,in,on,the等无实际意义的词
- Xy,z,mail,xyz,sohu,com
- StandardAnalyzer
- 混合分割,包括了去掉停止词,支持汉语
- xy&z,mail,[email protected]
4.3. 词 中文分词
- 单字分词
- 二分法
- CJKAnalyzer
- 词典分词
- 中科院ICTCLAS,C++开发(JNI)
- JE分词,由java写成je-analysis-1.4.0.jar
5. Query Parser
5.1. 改变QueryParser 默认的布尔逻辑
- QueryParser默认的逻辑是“或”.可以通过setDefaultOperator方法来改变默认的布尔逻辑。
Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer(); QueryParser qp = new QueryParser("contents", analyzer); qp.setDefaultOperator(QueryParser.AND_OPERATOR); Query query = qp.parse(queryString);5.2. Query Parser Syntax 法 语法
- Java AND Struts
- Java OR Struts
- Java – Struts
- Java NOT Struts
- 通配符
jav*/contents:jav*对于一个短语来说,如果想让QueryParser不对其进行分词,则加上引号
- 不加引号
+contents:man +contents:always +contents:remember +contents:love +contents:because +contents:romance +contents:only - 加引号
contents:"man always remember love because romance only"5.3. Query Parser Syntax
- Overview
- Terms
- Fields
- Term Modifiers
- Wildcard Searches
- Fuzzy Searches
- Proximity Searches
- Range Searches
- Boosting a Term
- Boolean Operators
- AND
- +
- NOT
- -
- Grouping
- Field Grouping
- Escaping Special Characters
5.4. 课堂练习:熟悉搜索语法
6. 索引
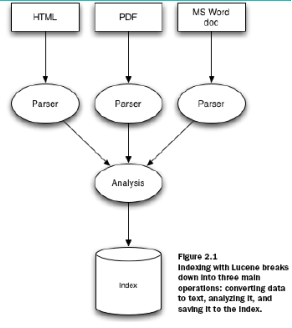
6.1. 使用Lucene索引分为三个主要步骤:
- 将数据转化为文本,分析,将它保存至索引
- 尽管大多程序关心的是添加Document到Lucene索引中,一些也需要清除它们。例如,报纸出版社可能只想在可搜索的索引中保留最近一个周的有价值的新闻。另外的程序可能想清除所有包含特定单词的Document。
- Document的删除是由IndexReader来完成的。这个类并不立即从索引中删除Document。它只做个删除的标志,等待IndexReader的close()方法调用时真正的Document删除。
IndexReader reader = IndexReader.open(dir); reader.delete(1); reader.isDeleted(1) reader.hasDeletions() reader.maxDoc(); reader.numDocs();6.2. maxDoc()和numDocs()
- IndexReader经常混淆的两个方法的不同:maxDoc()和numDocs()。
- maxDoc()返回下一个可用的内部Document号,
- numDocs()返回索引中的Document的数目。
- numDocs()能够立即感知到Document的删除,而maxDoc()不能。
- 每个Lucene的Document有个唯一的内部编号。这些编码不是永久分配的,因为Lucene索引分配时在内部重新分配Document的编号。因此,你不能假定一个给定的Document总是拥有同一个Document编号。
6.3. delete(Term)
- 除了我们通过指定Document编号来删除单个Document之外,你可以用IndexReader的delete(Term)方法删除多个Document。使用这个删除方法,允许你删除所有包含指定Term的Document。
- 例如,为了删除city字段中包含单词Amsterdam的Document,你可以这样用IndexReader:
IndexReader reader = IndexReader.open(dir); reader.delete(new Term(“city”, “Amsterdam”)); reader.close();6.4. 恢复Document
- 因为Document的删除延迟到IndexReader实例关闭时才执行,Lucene允许程序改变想法并恢复已做删除标记的Document。
- 对IndexReader的undeleteAll()方法的调用通过清除索引目录中的.del文件来恢复所有删除的Document。所以在关闭IndexReader实例关闭之后Document就保留在索引中了。
- 只能使用与删除Document时同一个IndexReader实例,才能调用undeleteAll()来恢复Document。
6.5. 更新索引中的Document
- “如何才能更新索引中的文档?”是一个在Lucene用户邮件列表中经常问的问题。Lucene并没有提供更新方法;Document必须首先从索引中删除然后再重新添加它
- 如果你需要删除和添加多个Document,最好是进行批操作。按以下步骤:
- 默认情况下,所有的Document都没有增量――或者更恰当地说,它们都有相同的增量因数1.0。通过改变某个Document的增量因数,你可能让Lucene认为它比索引中的其他Document更重要或不重要。
- 执行这些的API只需一个方法,setBoost(float)
Document doc = new Document(); …… doc.setBoost(1.5); …… writer.addDocument(doc);6.7. Field增量
- 就象你可以增量Document一样,你也可以增量个别的字段。
- 当你增量Document时,Lucene内部使用相同的增量因数增量它的每个字段。 field.setBoost(1.2);
7. 排序
7.1. Lucene默认按照文档得分进行排序
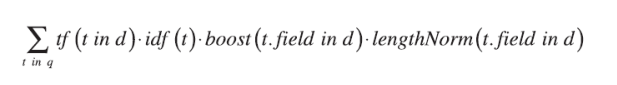
Lucene uses this formula to determine a document score based on a query.
- tf(t in d)词条t在文档d中出现的词频
- idf( t )词条t在文档中的倒排词频
- boost(t.field in d)在索引过程中设置的字段参数
- lengthNorm(t.field in d)字段的标准化值,表明在字段中存储了多少词条,这个数值是在索引过程中计算出来的,并且也存储在索引中
- coord(q, d)协调因子,它的计算是基于文档d中所包含的所有可供查询的词条数量
- queryNorm(q)在给出每个查询条目的方差和后,计算某查询的标准化值
7.2. explain方法
public Explanation explain(Query query, int doc)
- 该方法返回一个Explanation 类型的对象。 Explanation 类的toString方法提供的信息,能否将一个文档的得分情况详细的例举出来。
String explain = searcher.explain(query, hits.id(i)).toString(); System.out.println(explain);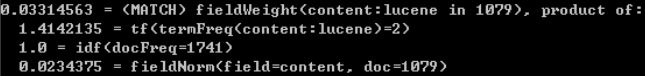
7.3. 改变文档的得分
- 除了内置的得分算法外,Lucene还提供了一种方法来改变每个文档的得分。
- 初始化Document后,可以使用Document的setBoost方法来改变一下文档的boost因子。这种做法的实际目的是将文档的得分乘以这个因子,以这个新的数作为文档的得分。
public void setBoost(float boost)Sets a boost factor for hits on any field of this document. This value will be multiplied into the score of all hits on this document. Values are multiplied into the value of Fieldable.getBoost() of each field in this document. Thus, this method in effect sets a default boost for the fields of this document.7.4. sort排序
- 如何对某个特定的field进行排序?
- 实例化一个Sort对象,并使用Searcher的Search(Query,Sort)方法。
- org.apache.lucene.search.Searcher
search(Query query, Sort sort)Returns documents matching query sorted by sort.
- org.apache.lucene.search.Sort
- SortField 构造方法
- public SortField(String field, int type, boolean reverse)
- org.apache.lucene.search.Sort
8. 过滤
8.1. 搜索的过滤器
- 搜索的过滤器可以减小搜索的范围,即使搜索的结果匹配,但由于文档已经被过滤,所以仍然不会返回给客户。比如可以用它来实现一种机制,保护某些文档没法被检索到。
- 所有的过滤器都来自一个抽象的基类org.apache.lucene.search.Filter
public abstract BitSet bits(IndexReader reader) throws IOExceptionjava.util.BitSet此类实现了一个 按需增长的位向量。位 set 的每个组件都有一个 boolean 值 .java.util.BitSet类提供了一个public BitSet(int nbits)构造方法 创建一个位set,它的初始大小足以显式表示索引范围在 0 到 nbits-1 的位。所有的位初始均为 false。
- Lucene以两种取值(true、false)来代表文档是否被过滤
| idx | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 值 | F | T | F | T | T | F | T | T | F | F | T | T | F | F |
8.2. 一个简单的Filter
共设置3中安全级别,要求将安全级别最高的文档过滤掉
SECURITY_ADVANCED = 0,SECURITY_MIDDLE 1,SECURITY_NORMAL = 2,
public class AdvancedSecurityFilter extends Filter { public static final int SECURITY_ADVANCED = 0; // 安全级别的常量 public BitSet bits(IndexReader reader) throws IOException { final BitSet bits = new BitSet(reader.maxDoc()); // 首先初始化一个BitSet对象 bits.set(0, bits.size() - 1); // 先将整个集合置为true,表示当前集合内的所有文档都是可以检索到的. Term term = new Term("securitylevel", SECURITY_ADVANCED + ""); // 最高安全级别. TermDocs termDocs = reader.termDocs(term); // 从索引中取出最高安全级别的文档 while (termDocs.next()) { bits.set(termDocs.doc(), false); // 遍历每一个文档,将相应的set置为false } return bits; } }8.3. 一个简单的Filter的另一种实现方法
上一个例子中,使用了IndexReader的较底层的API,还可以在bits方法中进行一次查询,来获得想要的结果.
```java public class AdvancedSecurityFilter extends Filter { public static final int SECURITY_ADVANCED = 0; //安全级别的常量
public BitSet bits(IndexReader reader) throws IOException {
final BitSet bits = new BitSet(reader.maxDoc()); //首先初始化一个BitSet对象 bits.set(0, bits.size() - 1); //先将整个集合置为true,表示当前集合内的所有文档都是可以检索到的. Term term = new Term("securitylevel", SECURITY_ADVANCED + ""); //最高安全级别. // 初始化一个IndexSearcher对象, //查找securitylevel这个field的值是SECURITY_ADVANCED的文档 IndexSearcher searcher = new IndexSearcher(reader); Hits hits = searcher.search(new TermQuery(term)); for (int i = 0; i < hits.length(); i++) { bits.set(hits.id(i), false); //遍历每一个文档,将相应的set置为false } return bits;} }
### 一个简单的Filter:在搜索时应用过滤器
- org.apache.lucene.search.Searcher 提供了在检索中应用Filter的方法
- public Hits search(Query query, Filter filter) ……
- public Hits search(Query query, Filter filter, Sort sort)
```java
Hits hits = searcher.search(q,new AdvancedSecurityFilter()) ;
8.4. 内置的过滤器
- org.apache.lucene.search.Filter 提供了几个内置的过滤器
- Direct Known Subclasses:
BooleanFilter, CachingWrapperFilter, ChainedFilter,ModifiedEntryFilter, PrefixFilter, QueryWrapperFilter, RangeFilter,RemoteCachingWrapperFilter, TermsFilter8.5. RangeFilter
RangeFilter用于将检索结果限定在某个给定的Field值的范围内
```java // fieldName - field 名称 // lowerTerm – 范围下界 // upperTerm – 范围上届 // includeLower – 下届是否包含在范围内 // includeUpper – 上届是否包含在范围内 // RangeFilter 提供了静态方法来得到”无上边界/无下边界”的 public RangeFilter(String fieldName, String lowerTerm, String upperTerm, boolean includeLower, boolean includeUpper)
// RangeFilter. public static RangeFilter Less(String fieldName, String upperTerm) public static RangeFilter More(String fieldName, String lowerTerm)
```java
RangeFilter filter = new RangeFilter("publishdate","1970-01-01","1990-01-01",true,true);
8.6. QueryFilter 结果中查询
QueryFilter 使用很简单, 其构造函数接受一个Query 对象, 该Query 对象可询 以看作是前一次查询, 只要在本次查询时将所构造的QueryFilter 对象作为可 参数传入即可
// Deprecated. use a CachingWrapperFilter with QueryWrapperFilter
Term begin = new Term("publishdate","1970-01-01");
Term end = new Term("publishdate","1990-01-01");
RangeQuery q = new RangeQuery(begin,end,true);
QueryFilter filter = new QueryFilter(q);
Term normal = new Term("securitylevel",SECURITY_ADVANCED+"");
TermQuery query = new TermQuery(normal);
IndexSearcher searcher = new IndexSearcher(PATH);
Hits hits = searcher.search(query,filter);